

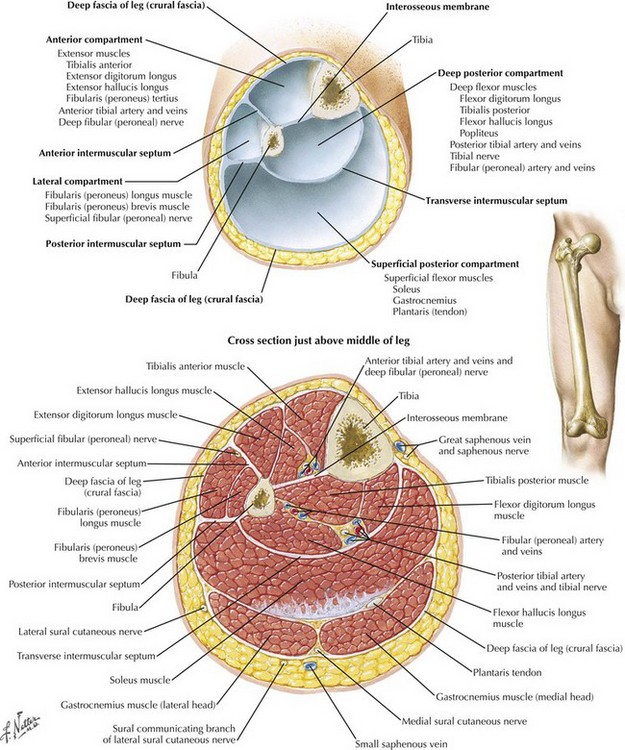
The lateral leg compartment is narrow and contains the FLM, FBM, the common and superficial fibular nerves, and branches of the anterior tibial artery and fibular artery. The lateral leg compartment is isolated from the other leg compartments by the deep (crural) fascia of the leg laterally, the fibula medially, the anterior intermuscular septa anteriorly, and the posterior intermuscular septa posteriorly. The muscles in the leg are divided into four compartments, the anterior, lateral, posterior superficial, and posterior deep, by intermuscular septa. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the anatomical makeup of the lateral leg compartment, in order to understand potential pathologies and their implications on the function of the lower extremity. Compartment syndrome can have devastating consequences if not managed appropriately, including ischemic necrosis of the lateral leg compartment structures, causing leg dysfunction and potentially leg loss. Additionally, patients may sustain acute compartment syndrome from direct trauma, inversion ankle sprains, prolonged surgical lithotomy position, and other general medical causes. Due to the compact nature of the lateral leg compartment, it is prone to compartment syndrome, with 13.9% to 34.4% of leg pain being associated with chronic exertional compartment syndrome (CECS). Additionally, variations in the spitting of the common fibular nerve into the superficial fibular nerve and deep fibular nerve have been reported, as well as variations in the course and splitting of the superficial fibular nerve. The lateral leg compartment is highly variable morphologically and may have variants such as the fibularis quartus (FQ) muscle, fibularis digit quanti (FDQ), variable insertions of the fibularis brevis tendon (FBT), and supernumerary fibularis muscle bellies. The anterior tibial and fibular arteries, and superficial fibular nerve provide neurovascular supply to the lateral leg compartment. The primary function of the FLM and FBM is foot and ankle eversion, with a secondary function of foot and ankle plantarflexion and maintenance of the foot transverse and lateral arches. Structures with the term “peroneal” have been replaced with “fibular” for anatomical accuracy. The operation is similar to the one used to treat acute compartment syndrome.Containing the fibularis longus muscle (FLM) and fibularis brevis muscle (FBM), common fibular and superficial fibular nerves, and branches of the anterior tibial and fibular arteries, the lateral leg compartment is one of the four compartments of the leg. If your symptoms do not improve after trying these things, surgery may be an option. use inserts (orthotics) in your shoes if you start running again.use anti-inflammatory painkillers to reduce the pain and discomfort.avoid the activity that caused them – if you run, switching to a low-impact exercise, such as cycling, may help.Treatment is often not needed for compartment syndrome that develops gradually.
ANTERIOR POSTERIOR COMPARTMENTS OF LEG FULL
You may also need physiotherapy to help regain full movement in the affected part of your body.
ANTERIOR POSTERIOR COMPARTMENTS OF LEG SKIN
This is known as a skin graft.Īfter the operation, you’ll have medicine to help ease any pain.
Sometimes, skin may need to be removed from another part of the body and used to cover the wound. During a fasciotomy, the surgeon makes cuts around the muscle to relieve the pressure. This type of surgery is called a fasciotomy. If compartment syndrome happens suddenly, you’ll need surgery as soon as possible to relieve the pressure in the muscle. Treatment for compartment syndrome depends on whether it happens suddenly or comes on gradually. Measuring the pressure inside a muscle is usually only recommended if your symptoms and other test results suggest compartment syndrome. compartment pressure measurement – a needle connected to a pressure monitoring device is inserted into your muscle before and after exercise to measure the pressure inside it.MRI scans while you’re resting and while you’re exercising.an X-ray to check if you’ve broken a bone.If the GP thinks you may have compartment syndrome, you may be referred to a specialist for tests. you keep getting pain, numbness, swelling, or have difficulty moving a part of your body when you exerciseĪ GP can help find out if the pain is caused by compartment syndrome or another condition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
